Running a Parallel Replica Job#
A sample parallel replica simulation can be found in the directory:
examples/parallel-replica/. Two input files config.ini and pos.con are
required for EON simlution.
The example system is the diffusion of an Al adatom on the Al(100) surface. A snapshot of the system is given below:
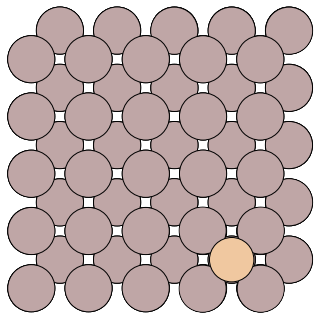
Al adatom on the Al(100)#
The config.ini file will run a parallel replica job with 2 replicas on one local core.
[Main]
job = parallel_replica
temperature = 500 ; temperature of the MD simulations
random_seed = 1024
[Potential]
potential = eam_al ; embedded atom method potential for aluminum
[Communicator]
type = local ; run the client locally
client_path =../../client/client ; $PATH for the client binary
number_of_cpus = 1 ; number of jobs to run locally
num_jobs = 2 ; total number of trajectories to run
[Dynamics]
time_step = 2.0 ; timestep of the MD simulation (in fs)
time = 12000.0 ; total number of MD steps to run
thermostat = andersen ; Andersen thermostat with Verlet algorithm
andersen_alpha = 0.2 ; collision strength in the andersen thermostat
andersen_collision_period = 10.0 ; collision period of andersen thermostat (in fs)
[Parallel Replica]
dephase_time = 200 ; number of steps used to decorrelate the replica trajectories.
state_check_interval = 3000 ; number of steps between quanches to check if a new state is found
state_save_interval = 200 ; number of steps recorded to a buffer array to refine the transition time
post_transition_time = 200 ; number of additional MD steps run after a new state is found
stop_after_transition = false ; flag to stop the job when a new state is found
[Optimizer]
opt_method = cg ; use the conjugate gradient optimizer
converged_force = 0.005 ; stop optimizations when the max force per atom reaches 0.005 eV/A
Now we can run the trajectory by executing the command python -m eon.server
EONgit/examples/parallel-replica via 🅒 eongit
➜ python -m eon.server
Eon version: 1321976b
Simulation time: 0.000000e+00 s
State list path does not exist; Creating: .//states/
Registering results
Processed results: 0
Time in current state: 0.000000e+00 s
Simulation time: 0.000000e+00 s
Queue contains: 0 searches
Making: 2 searches
Job finished: .//jobs/scratch/0_0
Job finished: .//jobs/scratch/0_1
Created: 2 searches
Then use the -n flag to register the result::
EONgit/examples/parallel-replica via 🅒 eongit
➜ python -m eon.server -n
Eon version: 1321976b
Simulation time: 0.000000e+00 s
Registering results
Found transition with time: 5.000e-12 s
Cancelled 0 workunits from state 0
Processed results: 0
Currently in state: 1
Time in current state: 0.000000e+00 s
Simulation time: 5.000000e-12 s
Queue contains: 0 searches
Making: 0 searches
Information from the trajectory is written in the dynamics.txt file:
➜ cat dynamics.txt
step-number reactant-id process-id product-id step-time total-time barrier rate energy
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 1 5.000000e-12 5.000000e-12 0.000000 0.000000e+00 -472.909569
More information is obtained by running a few more times:
➜ for i in {0..2}; python -m eon.server; done
Eon version: 1321976b
Simulation time: 5.000000e-12 s
Registering results
Processed results: 0
Time in current state: 0.000000e+00 s
Simulation time: 5.000000e-12 s
Queue contains: 0 searches
Making: 2 searches
Job finished: .//jobs/scratch/1_2
Job finished: .//jobs/scratch/1_3
Created: 2 searches
Eon version: 1321976b
Simulation time: 5.000000e-12 s
Registering results
Found transition with time: 2.000e-12 s
Cancelled 0 workunits from state 1
Processed results: 0
Currently in state: 2
Time in current state: 0.000000e+00 s
Simulation time: 7.000000e-12 s
Queue contains: 0 searches
Making: 2 searches
Job finished: .//jobs/scratch/2_4
Job finished: .//jobs/scratch/2_5
Created: 2 searches
➜ python -m eon.server -n
Eon version: None
Simulation time: 7.000000e-12 s
Registering results
Found transition with time: 3.000e-12 s
Cancelled 0 workunits from state 2
Processed results: 0
Currently in state: 3
Time in current state: 0.000000e+00 s
Simulation time: 1.000000e-11 s
Queue contains: 0 searches
Making: 0 searches
➜ cat dynamics.txt
step-number reactant-id process-id product-id step-time total-time barrier rate energy
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 1 5.000000e-12 5.000000e-12 0.000000 0.000000e+00 -472.909569
1 1 0 2 2.000000e-12 7.000000e-12 0.000000 0.000000e+00 -472.909577
2 2 0 3 3.000000e-12 1.000000e-11 0.000000 0.000000e+00 -472.909572
Detailed information of the simulation is stored in the folder states. where
the geometric and energy of the visited states are stored in the sub-folder
labeled as state id. You can find the geometric of the prodcut in
states/1/reactant.con/, a snapshot is shown below:
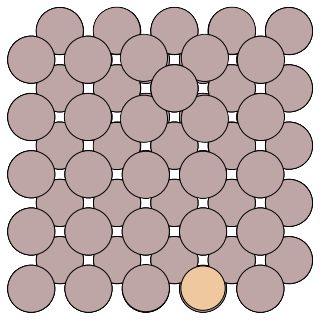
Al adatom on the Al(100)#
Compared to the reactant geometric, we can tell that the transition we found follows the exchange mechanism.
Adding Hyperdynamics#
You can turn on the hyperdynamics method by adding the following section to your config.ini file:
[Hyperdynamics]
bias_potential=bond_boost ; bond_boost bias potential
bb_boost_atomlist=20,26,50,56,150 ; atoms that are boosted in the bias potential
bb_rcut=3.0 ; boost radius
bb_rmd_time=100.0 ; MD time to obtain the equilibrium configuration
bb_dvmax=0.4 ; magnitude of the bond-boost bias potential
bb_stretch_threshold=0.2 ; defines the bond-boost dividing surface
bb_ds_curvature=0.95 ; curvature near the bond-boost dividing surface, it should be <= 1; a value of 0.9-0.98 is recommended
All other settings and output infomation are as in a regular parallel replica dynamics simulation.